|


In order to promote
decomposition of wasted tires and wasted rubbers,
wash and dry the pieces mentioned above, and then
transport and insert into preheater to get recycled
materials in good quality.
At same time, insert catalyst initiator into the
catalyst initiator insertion hole in order
to promote active decomposition.
Catalyst initiator should be continuously inserted
until the first decomposition is executed. If
first decomposition is executed, it will keep
operating decomposition although you stop inserting
catalyst initiator.
If you do not want to secure GAS generated since
then, use it for heat source. GAS processed through
condenser is stored at TANK as OIL.
CARBON BLACJ(C/B) and steel cores decomposed into
original materials are separated through M/S,
and then they are packed and stored for delivery.

1. Continuous low temperature decomposition is
enabled.
2. Generated materials are restored to original
materials.
3. It is quite competitive with its low operation
expense and generated materials.
4. Since it uses GAS generated by itself, there
is no burden for fuel expense.
5. Since it decomposes at low temperature, manufacturing
expense is low and life cycle of the device is
long.
6. No environmental pollution.
7. For foreign countries (United States, Thailand,
Canada, Australia, EU countries and others), it
is quite economical since their operation expense
is higher than US$2.

|
|
|
|
|
Wasted Tires and Synthetic Rubbers |
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
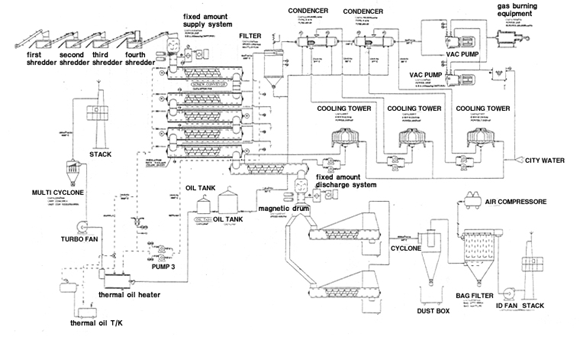
Waste
tire cutting process at item
1 → Transport them to waste
accumulator after washing
and drying procedure → Insert
into main decomposition chamber
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel insertion in item 2, preheating process → Sublimation process is performed at main decomposition chamber → Separated gas is compressed and transported to concentration device in item 2, remaining CARBON BLACH and other solid state materials and steel cores are transported to separation process in item 3 |
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Transport to storing tank after concentrating into oil at condenser and related device of item 2. |
In
item 3,
③ Steel core and CARBON BLACK
separation process
④ Directly transport and pack
after going through CARBON BLACK
differential pulverizing process
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Waiting for delivery at oil storing tank |
Steel → Store → Waiting for Delivery |
Waiting for delivery after packing in certain unit |
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Oil Delivery
|
Steel Delivery
|
CARBON BLACK Delivery
|
|

|
No.
|
Item
|
Based on Tires of 50t in a Day
|
Wasted
Rubbers 25ton
Tires 24ton
|
|
Generated Quantity
|
Amount (Won)
|
|
1
|
OIL (Annual Production)
|
6,000,000ℓ
|
2,220,000
|
|
|
2
|
CARBON BLACK (Annual Production)
|
4,200ton
|
924,000
|
|
|
3
|
STEEL
|
1,470ton
|
132,000
|
|
|
4
|
Wasted Tire Handling Expense
|
825,000
EA
|
412,500
|
150
Days
|
|
5
|
Wasted Rubber Handling Expense
|
7,500ton
|
1,050,000
|
150
Days
|
|
|
Total Annual Profit
|
|
4,738,500
|
|
 Conversion Basis
Conversion Basis |
- Based on oil sales price of 1ℓ x 370 won
- Based on oil generation amount of 400ℓ for tires of 1t
- Based on CARBON BLACK generation amount of 280kg for tires of 1t, Based on sales price of 1t x 220,000 won
- Based on steel generation amount of 98kg for tires of 1t and sales price of 1kg x 90 won
- Based wasted tire handling expense for passenger cars of 500 won for each tire (based on the price in 1999)
- Based on 110 EA for tires of 1T (average weight of 8.9kg)
- Wasted rubber handling expense of \140,000/t
|

|
|
MICHENAE
|
ATR
|
OXFORD
|
CONRAD
|
ONODA CEMENT
|
ENERGECO
|
T.R. ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGY
|
|
Handling Method
|
Dried gas
|
Thermal decomposition
|
Incineration
|
Thermal decomposition
|
Incineration
|
Incineration
|
Thermal decomposition
|
|
Location
|
Japan
|
United States
|
United States
|
United States
|
Japan
|
Italia
|
Korea
|
|
Quantity of Tire Handling
|
200T/D
|
50T/D
|
300T/D
|
24T/D
|
72T/D
|
60T/D
|
50T/D
|
|
Operating Tem.
|
About
500℃
|
540~650℃
|
|
482~537℃
|
1,500~2,000℃
|
|
200~250℃
|
|
Gene
rated Mater
ials
|
OIL
GAS
STEEL
|
0.35kg/kgTIRE
0.6N㎡/kgTIRE
0.3kg/kgTIRE
0.1kg/kgTIRE
|
0.42kg/kgTIRE
0.44N㎡/kgTIRE
0.29kg/kgTIRE
0.1kg/kgTIRE
|
Electricity 300KW/H
|
0.35kg/kgTIRE
Electricity
5000KW/H
0.26kg/kgTIRE
|
|
STEAM:20T/H
(20KG)
400KG/H
|
Oil
& gas or both
in option
0.25kg/kgTIRE
0.1kg/kgTIRE
|
|
Required Site
|
|
About 9,917.4m2
|
|
|
|
About 1,983.5m2
|
About 1,322.3m2
|
|
Operating Expense
|
|
Requires 55 operators
|
|
Requires 6 operators
|
|
5,000KW/H of electricity and 11 operators are required
|
Requires 5 operators
|
|
Tire Handling Investment by TON/D
|
121 million won(T/D)
|
136 million won(T/D)
|
283 million won (T/D)
|
146 million won (T/D)
|
|
213 million won(T/D)
|
100
million won (T/D)
|
|
Characteristics
of Process
|
Use whole tiresLow operation expenseLONE SELF-COOLINGSYSTEMFine heat efficacy as a vertical furnace
|
Requires tire cutting device (increase expense for power)Requires too much operation expense Requires upgraded facility for CARBON
|
User tires Requires great amount of investment for pollution preventing facility STOKERincinerator type Requires too much operation expenseIncineration process for handling tires is prohibited by domestic environmental regulations
|
Requires tire cutting deviceInstalls large PLANTNo sales recordGenerating power with STEAM is possible
|
Substitute 15% of fuel with wasted tires Use whole tires Requires no pollution preventing facility Using large tires is possible Because of efficacy value difference of soft coal alternative furnace, performance level is low
|
ROTARYKLIN typePrice is high and overall facility efficacy rate is low Impossible to install single large plant Not allowed by environmental regulations
|
Includes cutting device Low operation expense Simple facility Secondary pollution preventing device is not necessary Decomposes to original materials by applying new principles
|
|
Technical Reliability
|
Highly reliable
|
Highly reliable
|
Highly reliable
|
Technology in distribution stage
|
Highly reliable
|
Highly reliable
|
Decomposition to original materials
|
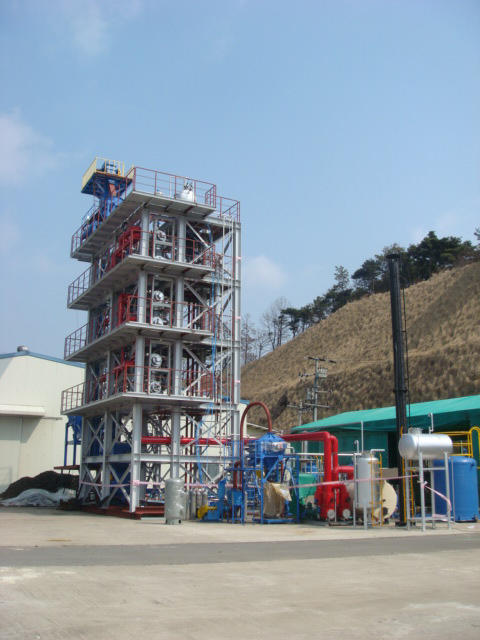
Click above picture for bigger image.
 |
![]()